By Jon Ipema
•
September 12, 2025
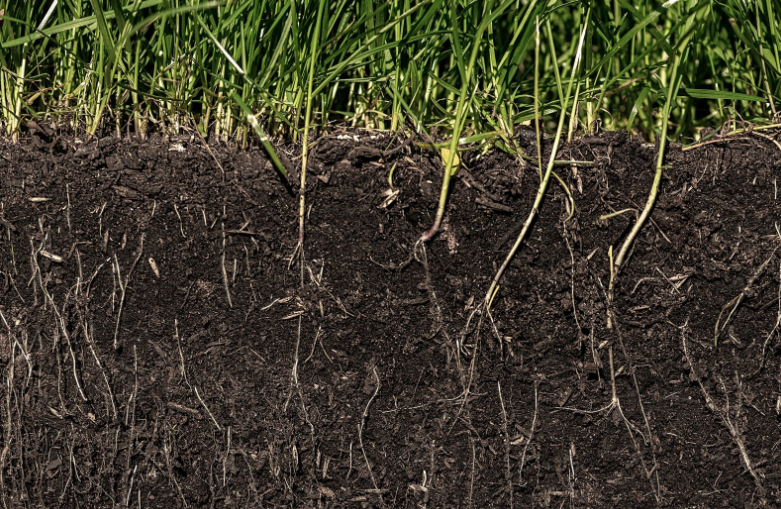
The goal of this article is not to berate other professionals; instead, it is to get a better understanding of how to get desired results while avoiding counterproductive measures that often impede progress, increase maintenance, and are detrimental to the goals of plant cultivation and land management. Often, attention is applied strictly to climate and aesthetics. The decisions are typically made based on whether a plant is known to survive in a particular zone and results from successful cultivation (often, photos of established plants). Although these are important issues, the results are often compromised by disregard for soil type, soil quality, maintenance requirements, desired results, and specific strengths and weaknesses of individual species and subspecies. Proper consideration of the process and costs of achieving desired outcomes can be oversimplified to the detriment of that outcome. Observing this time and again, a cycle has been noticed that seems to repeat itself. Analyzing this cycle has given insight into how to avoid this cycle and the frustration that goes along with it. Signs of this cycle are increases in maintenance, costs, and frustration while experiencing decreased aesthetics, plant health, and recurring issues. Here is an example: 1. A lawn does not appeal to its owner and steps are taken to improve the situation. 2 . The first step is often to incorporate a fertilization program. 3. A generalized fertilization program is implemented, with the primary focus being macro-nutrients for turf and weed control. 4. Initially this seems productive and seems to be leading to satisfactory results especially in the beginning of the season, when temperatures are lower and natural irrigation is sufficient. 5. As the season progresses and temperatures increase the results seem to diminish. The color of the lawn appears fair at best, weeds become more of an issue, and general satisfaction declines. Watering is increased, chemical applications to control weeds are rendered, and some choose to increase fertilization to achieve what seemed to be improving results earlier in the season. 6. During midseason, temperatures are at extremes, and the focus gets shifted to irrigation, with some increase to the length of time for irrigation but mostly on the frequency. 7. As the end of summer approaches, nighttime temperatures decrease, while temperatures during the day still feel extreme. Turf appears to be recovering and looking better. Weeds continue to be an issue and additional weed control measures are often taken, usually spot treating as even selective herbicides can damage turf in the heat of the day. At this point fungal issues appear and many opt to apply fungicides to control the matter. 8. Some satisfaction with weed control seems to take place although grassy weeds remain persistent and fungal issues come and go. Overall, the turf seems better than previous seasons and staying on the course seems to be the correct action for the next season. 9. Year 2 - In spring pre-emergent weed control is applied to keep grassy weeds controlled (primarily crabgrass). Patches of inconsistent turf seem to be taking hold, and the turf color continues to decline. Spring is often when other fungal issues are noticed, especially cold season fungal issues that take place throughout the winter (snow molds). 10. Increases in fertilizer are often recommended to return color to turf while weed control becomes a larger issue. Irrigation is more frequent, as it seemed to help the stressed turf during the previous season. 11. Although recommendations are followed, by midseason it is apparent that turf quality is not improving, there may be a noticeable “boost” to aesthetics for a short period after fertilization, but not much further. 12. When evening temperatures begin dropping but daytime temperatures are still high, fungal issues return. It may be recommended to add fungicidal applications to the fertilization program annually to “get ahead” of the problem. 13. Turf doesn’t seem to improve any further and is often declining at this point. During the 3rd season some owners begin looking at other options, but some stay on this course and continue, many of these individuals simply get accustomed to a subpar lawn. Others contemplate discontinuing service, as the programs appear to be a gimmick. 14. By the fourth season many have had enough. Many companies will continue to offer more services claiming that they will solve the issues. By this point the customers usually have had enough, even more convinced that their lawn will just never look the way they would like. This pattern may vary from what is indicated above. The main point is that this system is reactive rather than proactive. Certain people experience a degree of success. This is typically short-lived, and they don't even realize the added maintenance and costs. My experience is that these results vary from lawn to lawn, which are not replicable, and lack consistency. This brings us to the main point of this article…How do we stop the cycle and get the results we want, without constantly increasing the need for more maintenance? Let's start at the same point as we did earlier. 1. A lawn does not appeal to its owner and steps are taken to improve the situation. 2. Soil tests are taken to provide information as to what is going on currently, how to adjust, and what type of grasses fit the purpose of the lawn. 3. Soil amendments are made to correct micro-nutrient deficiencies and correct soil chemistry. Aeration is completed to aid the microbial processes in the soil, reduce compaction, and maintain the thatch layer. Lawn is overseeded with turfgrass that fits the desired outcome, thrives in the climate, and resists disease. 4. Fertilizer program is implemented to address macronutrients and help maintain chemical adjustments performed in previous step. At the beginning of this process, pre-emergent weed controls should be avoided and only implemented in the future if annual weeds are an issue. Even then I personally am not a proponent of preemergent weed control in turf, unless absolutely necessary as this hinders seed germination and causes issues with overseeding. 5. Instructions are given on maintenance information. Turfgrass needs to be maintained at a certain height and cut at regular intervals to maintain that height. Sharp blades and maintained equipment are important for turf grass health. This thickens the grass not only for aesthetic purposes, but also for weed control. 6. In spring when conditions are optimum for turf grass growth, the desired grass species will begin to take hold. As temps increase and are less favorable to the other grasses, this will become the dominant. With the corrections in the soil chemistry and condition this species will thrive, not allowing area for weeds to encroach. This is not to say weed control is not necessary, but it is drastically minimized. 7. Aeration needs to be performed on a regular basis, 1 to 2 times a year minimum, based on grass species, soil conditions, thatch conditions, and activities on the turf. 8. As the heat of the summer stresses the turf grass, correct watering is pertinent. Root systems of all plants require water, but they also require oxygen. A flooded root system will kill plants. Less frequent, deep watering is what plants including turf need. Turf grass varieties that are more tolerant of temperature extremes are the best solution to this issue. As these grasses grow and begin to dominate the turf ecosystem, other non-desirable plants will not have room to get a foot hold, limiting the need for weed control. Short frequent irrigation creates the environment for fungal disease. Without fungal disease the use of fungicide would be minimal if not irrelevant, avoiding the damage to mycorrhizae. These beneficial fungi aid in oxygen and nutrient transfer in root systems. 9. Year 2 - Turf appearance drastically improves as does the health of the grasses. Soil amendments are not necessary unless problems exist. Soil test should be done regularly (I recommend every 3 years, unless issues are present). Aeration and overseed are recommended in spring and fall, continue to feed (general purpose fertilizer, 4 application slow release sulfur coated urea), and continue maintenance as described above. 10. Lastly, enjoy. Healthy plants resist disease. Working with nature, controlling what we can, and mitigating what we can’t is the answer to all turf and landscaping. Overall maintenance will be far less chaotic as the days of chasing symptoms will come to a close. Any issues that arise can be dealt with systematically. In summary, the goal of any service is to meet the desires and needs of the owner. Quite frequently, services are performed without proper diagnostic procedures like soil tests. Neglecting proper diagnostics is the main way variables are added to the process, complicating the procedure to obtain the desired result. This can be avoided by using a scientific systemic approach. Although routine applications of turf fertilizer are recommended for most grass types, incorrect applications can cause more harm than good. This includes incorrect product choice, wrong application rate, or incorrect timing. Sometimes this is done inadvertently, like when an operator is unfamiliar with a piece of equipment, or an applicator neglects to research soil type, soil quality, soil tests, turf species, watering habits, common issues in the area, or there is unfamiliarity with the products or active ingredients of products. Time and again, additional problems are caused by these miscalculations. These issues cost the owner money, time, and lost enjoyment, while adding additional sellable services benefiting only the contractor. Please note that this is not always done intentionally. Many fertilizer and landscape contractors simply do not know the intricacies of plant life and often attempt to simplify the subject to the point that it is, in fact, made more difficult (as described in the above cycle). Although this is often done unintentionally, mainly due to incompetence (not using the term as a derogatory; instead: “inability to do something successfully; ineptitude”), I have seen a more deceptive side as well. This involves leaving the customers in the dark as to what is being done, stringing them along year after year, and never seeing any improvement. One way to spot this is when the “professional” continues to change the approach without explanation. This indicates a lack of understanding of the subject, and they are essentially using a ‘guess and check’ method on your dime. This approach involves selling services without regard to results. The Green Advantage approach is as follows: 1. Discuss with the client to discover their desired result. 2. Inspect. Gather data. Check growing conditions, acquire samples (soil, sometimes branches or leaves) 3. Analyze the data. Proper identification of disease cannot be understated. Is it biotic or abiotic? Are the growing conditions correct? Is the watering schedule causing issues? 4. Separate controllable and uncontrollable factors. Make plans to adjust the controllable factors and mitigate the uncontrollable factors. a. An example of a controllable factor would be making soil amendments for imbalances discovered in the soil test. b. An example of an uncontrollable factor would be weather/climate/temperature range. Although we cannot change this, we can mitigate this by choosing the correct plants for the climate. c. This is where the ‘economic threshold’ comes into play. This is a number that is different for each and every one of us. It is the balance between desired results and the cost of getting there. It is easiest to visualize when it comes to farming: A disease is found on a crop, the cost to treat the disease is X. Y is the amount of crop that will be forfeited if no treatment is performed. If Y>X, then treatment would pass the economic threshold. This is a little more difficult with aesthetic plants as the economic threshold varies greatly from person to person. 5. Implement the plans. 6. Monitor the results. 7. Reanalyze and be sure that results are in line with desired results and that desired results have not changed. Final thoughts. Honesty and integrity are the foundation of all good relationships. The relationships we have with our clients are no different. We are grateful for them and we treat them with dignity and respect. Thank you to all The Green Advantage customers and team members!! Jon Ipema